A general-purpose machine learning framework for predicting properties of inorganic materials (预测无机材料性能的通用机器学习框架)
 Logan Ward, Ankit Agrawal, Alok Choudhary & Christopher Wolverton
Logan Ward, Ankit Agrawal, Alok Choudhary & Christopher Wolverton
npj Computational Materials 2, Article number: 16028 (2016)
doi:10.1038/npjcompumats.2016.28
Published online:26 August 2016
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
摘要:材料研究的一个非常活跃的领域,是设计自动发现新材料的方法,即机器自行学习而能从现有材料数据中自动产生预测模型。虽然之前的实例已证明了一些应用模型非常成功,但机器的自行学习可使更多的现有应用模型功能更为强大。为了更快地开发基于机器学习的模型投入应用,本研究创建了一个框架,适用于宽泛的材料数据领域。我们的方法是将化学属性作不同的列表,发现这样很适合于描述宽泛领域内各种不同的属性,我们的另一种创新方法是将数据集按相似材料组分区,以此提高预测精度。本文展示了我们这种新方法如何预测了结晶材料和非晶材料的多种属性,比如带隙能量和玻璃化能力。
Abstract: A very active area of materials research is to devise methods that use machine learning to automatically extract predictive models from existing materials data. While prior examples have demonstrated successful models for some applications, many more applications exist where machine learning can make a strong impact. To enable faster development of machine-learning-based models for such applications, we have created a framework capable of being applied to a broad range of materials data. Our method works by using a chemically diverse list of attributes, which we demonstrate are suitable for describing a wide variety of properties, and a novel method for partitioning the data set into groups of similar materials to boost the predictive accuracy. In this manuscript, we demonstrate how this new method can be used to predict diverse properties of crystalline and amorphous materials, such as band gap energy and glass-forming ability.
Editorial Summary
Machine learning: Searching for novel materials (机器学习寻找新材料)
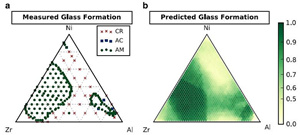
美国的研究人员开发了一个多功能的机器学习框架,以帮助寻找新材料。由西北大学的Christopher Wolverton和Logan Ward领导的研究人员,使用了机器学习技术训练电脑从已知材料数据中产生计算模型,以预测具有特殊性能的新材料。该技术的实用性通过两个实例得到证实,一个是从光伏应用的角度寻找新的结晶化合物;另一个是从玻璃形成三元合金相的角度寻找金属玻璃合金。新模型可通过优化机器学习算法和分区输入数据而创建,从而最大限度地提高某些参数的准确性。结合现有的对研究人员可利用的庞大材料数据,该技术有望自动并加速对新功能材料的寻找与发现。
Researchers in the United States have developed a versatile machine learning framework to aid the search for novel materials. Led by Christopher Wolverton and Logan Ward from Northwestern University, the researchers used machine learning techniques trained against known material data to generate models that predict the specific properties of new materials. The utility of the technique was demonstrated through searches for novel crystalline compounds for photovoltaic applications, and for metallic glass alloys based on the probability of glass formation for ternary alloys. New models can be created by optimizing the machine learning algorithm and partitioning input data to maximize the prediction accuracy for specific parameters. The technique has the potential to automate and accelerate the search for new functional materials using the large libraries of material data now available to researchers.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号