 Quantum–continuum simulation of underpotential deposition at electrified metal–solution interfaces (带电金属–溶液界面处欠电位沉积的量子–连续体模拟)
Quantum–continuum simulation of underpotential deposition at electrified metal–solution interfaces (带电金属–溶液界面处欠电位沉积的量子–连续体模拟)
Stephen E. Weitzner & Ismaila Dabo
npj Computational Materials 3, Article number: 1 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-016-0004-9
Published online:12 January 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
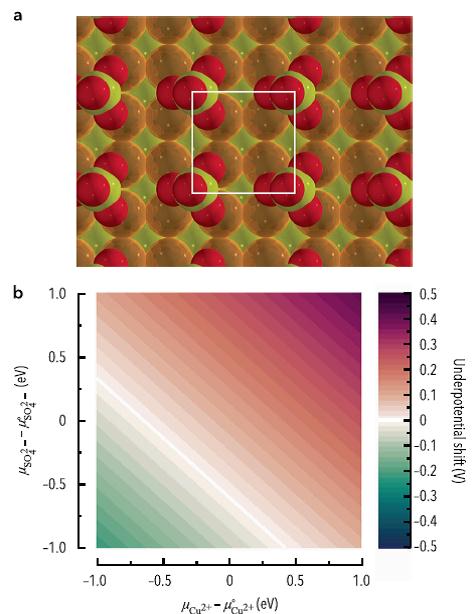
摘要:过渡金属离子的欠电位沉积是许多电合成途径的关键步骤。虽然欠电位沉积在原子水平上已得到深入研究,但运用第一性原理在真空条件下的计算结果有可能严重低估了欠电位沉积金属的稳定性。最近的研究结果表明,将共吸附阴离子考虑进来对欠电位沉积反应的描述更为可靠。除此之外,其他一些环境因素如电压引起的界面带电、溶液的离子活度等对欠电位沉积的影响等还亟待研究。本研究采用电化学界面的量子–连续体模型,探讨了真实电化学条件下,铜在金上的欠电位沉积。本研究报道了界面带电、浓度效应、阴离子共吸附对铜在金(100)表面的欠电位沉积层的稳定性所造成的影响。
Abstract: The underpotential deposition of transition metal ions is a critical step in many electrosynthetic approaches. While underpotential deposition has been intensively studied at the atomic level, first-principles calculations in vacuum can strongly underestimate the stability of underpotentially deposited metals. It has been shown recently that the consideration of co-adsorbed anions can deliver more reliable descriptions of underpotential deposition reactions; however, the influence of additional key environmental factors such as the electrification of the interface under applied voltage and the activities of the ions in solution have yet to be investigated. In this work, copper underpotential deposition on gold is studied under realistic electrochemical conditions using a quantum–continuum model of the electrochemical interface. We report here on the influence of surface electrification, concentration effects, and anion co-adsorption on the stability of the copper underpotential deposition layer on the gold (100) surface.
Editorial Summary
Thin films: How to overachieve at underpotentials (薄膜:不同欠电位条件下如何实现超稳定)
金属离子在欠电位条件下沉积在惰性金属表面形成可用于催化或传感的纳米材料。但在这个过程中所沉积的金属不稳定,常会被周围的液体所溶解。对此,来自美国宾州大学的Stephen Weitzner和Ismaila Dabo发展了一种程序解决量子-机械模拟方法中令人困扰的不稳定性。该方法可用来估计欠电位沉积时,铜离子在金表面沉积的稳定性。研究人员采用量子-连续体方法解释了溶剂效应,采用蒙特卡洛模拟理解带电金-水界面的带电状况对沉积的影响。这些计算结果提示了考虑界面电荷和共吸附离子等因素对精确模拟欠电位沉积的必要性。
The deposition of atomically thin metal films can be predicted with a comprehensive model incorporating realistic environmental factors. Nanomaterials used as catalysts and sensors are often produced by the spontaneous attachment of metal ions onto inert metal surfaces in the underpotential regime, where the depositing metal would normally dissolve in the surrounding liquid environment. Stephen Weitzner and Ismaila Dabo from the Pennsylvania State University have developed a procedure to resolve the perplexing inability of quantum-mechanical simulations to estimate the stability of underpotential deposits, such as copper ions onto gold surfaces. The researchers used a quantum–continuum approach to account for solvent effects and Monte Carlo simulations to understand how electrification of the gold–water interface impacts deposition. These computations revealed the need to include the interfacial charge and co-adsorbed ions to accurately simulate underpotential deposition.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号