 Facile measurement of single-crystal elastic constants from polycrystalline samples (以多晶样品测定单晶弹性常数的简便方法)
Facile measurement of single-crystal elastic constants from polycrystalline samples (以多晶样品测定单晶弹性常数的简便方法)
Xinpeng Du & Ji-Cheng Zhao
npj Computational Materials 3, Article number: 17 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0019-x
Published online:24 April 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
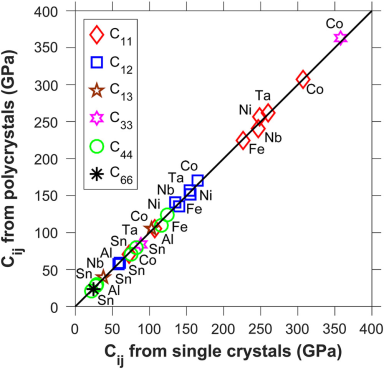
Abstract: Elastic constants are among the most fundamental properties of materials. Simulations of microstructural evolution and constitutive/micro-mechanistic modeling of materials properties require elastic constants that are predominately measured from single crystals that are labor intensive to grow. A facile technique is developed to measure elastic constants from polycrystalline samples. The technique is based upon measurements of the surface acoustic wave velocities with the help of a polydimethylsiloxane film grating that is placed on a polished surface of a polycrystalline sample to confine surface acoustic waves that are induced by a femtosecond laser and measured using pump-probe time-domain thermoreflectance. Electron backscatter diffraction is employed to measure the crystallographic orientation along which the surface acoustic wave propagates in each grain (perpendicular to the polydimethylsiloxane grating). Such measurements are performed on several grains. A robust mathematical solution was developed to compute the surface acoustic wave velocity along any crystallographic orientation of any crystal structure with given elastic constants and density. By inputting various starting values of elastic constants to compute the surface acoustic wave velocities to match experimental measurements in several distinct crystallographic orientations using an optimization algorithm, accurate elastic constant values have been obtained from seven polycrystalline metal samples to be within 6.8% of single-crystal measurements. This new technique can help change the current scenario that experimentally measured elastic constants are available for only about 1% of the estimated 160,000 distinct solid compounds, not to mention the significant need for elastic constants of various solid solution compositions that are the base of structural materials.
Editorial Summary
Mechanical properties: a simpler method for determining elasticity(机械性能:一种更简单的弹性测定方法)
美国科学家发明了一种可基于非完美样品测量材料弹性性能的方法。来自俄亥俄州立大学的Xinpeng Du和Ji-Cheng Zhao开发了一种用于基于多晶样品测量获得弹性常数的简易实验技术。材料的弹性或刚度在数学上可以用弹性常数来标定。目前测定材料弹性常数的主流实验方法都基于单晶样品。然而,单晶样品的制备过程相当费时费力,有时甚至根本制备不出来。与传统方法不同,Du和Zhao采用激光脉冲测定多晶样品中的所谓表面声波的速度,再结合他们发展的理论计算方法,即可根据材料的密度和测量出的声速确定材料的弹性常数。
A method for measuring the elastic properties of a material even with a less than perfect sample is demonstrated by scientists in the USA. Xinpeng Du and Ji-Cheng (J.C.) Zhao from The Ohio State University develop a simple experimental technique for obtaining elastic constants from polycrystalline samples. A material’s elasticity or stiffness properties are mathematically summarized by a series of parameters known as its elastic constants. Most experimental techniques for measuring these elastic constants require samples that are single-crystals. But these can be time consuming to produce or perhaps even impossible. Instead, Du and Zhao measure the velocity of so-called surface acoustic waves produced on a polycrystalline sample using pulses of laser light. They then develop a robust mathematical framework that can determine elastic constants based on material density and the measured velocities.
摘要:弹性常数是材料最基本的特性之一。材料的微结构演化模拟和本构/微力学模型的建立都需要弹性常数作为输入。目前测定材料弹性常数的主流实验方法都要借助单晶样品,而单晶样品的制备相当费时费力。本研究开发了一种基于多晶样品测量弹性常数的简易技术。该技术基于表面声波波速测量:将聚二甲基硅氧烷膜光栅放置在多晶样品的抛光表面上用来限制表面声波,以飞秒激光激发表面声波,并利用泵浦时域热反射技术进行测量。利用电子背散射衍射测定出表面声波的传输方向(垂直于光栅刻线方向)与晶粒具体晶向的对应关系。利用上述方法对几个不同的晶粒进行了测量。同时发展了一种可靠的数学方法计算表面声波的波速,只要给定晶体的弹性常数和密度,即可计算出表面声波在任意晶体结构中沿任意晶向传播的速度。以不同的弹性常数为输入,计算表面声波波速,并通过优化算法将计算结果与7种不同的金属多晶样品的实验测量值进行匹配,由此获得了这些材料的弹性常数,其数值相比单晶测量值误差在6.8%以内。由于现有的弹性常数测量的方法具有很强的局限性,其仅可用来估测160,000种固体化合物中的约1%化合物的弹性常数,更无法满足作为结构材料基础的各种固溶体组合物弹性常数的测定需求,因此本研究提出的新技术有可能改变这一现状。


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号