 Chemically intuited, large-scale screening of MOFs by machine learning techniques (通过机器学习技术辅以化学直觉,作大规模金属-有机框架材料筛选)
Chemically intuited, large-scale screening of MOFs by machine learning techniques (通过机器学习技术辅以化学直觉,作大规模金属-有机框架材料筛选)
Giorgos Borboudakis, Taxiarchis Stergiannakos, Maria Frysali, Emmanuel Klontzas, Ioannis Tsamardinos & George E. Froudakis
npj Computational Materials 3:40 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0045-8
Published online:02 October 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
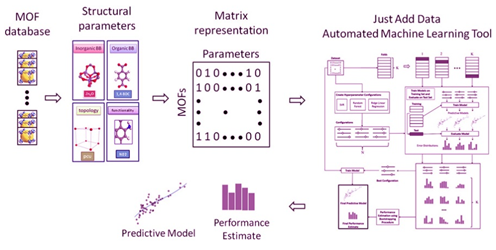
摘要:本研究报道一种新型计算方法,应用于机器学习技术,可对有储气性能的金属-有机框架材料(Metal–organic frameworks,MOFs)作大规模筛选。该方法结合化学结构导向,在第一原理方法的计算准确性和经典方法的计算速度之间作了平衡。结果表明,采用机器学习方法和自动化分析方案,MOF的化学性质确实是可预测的(随机而不是确定的),其预测准确性随着样本量的增加而增加。初步研究结果表明,这种方法不仅有望用于储气MOF,也有望用于其他涉及材料科学的诸多应用方面。
Abstract: A novel computational methodology for large-scale screening of Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) is applied to gas storage with the use of machine learning technologies. This approach is a promising trade-off between the accuracy of ab initio methods and the speed of classical approaches, strategically combined with chemical intuition.The results demonstrate that the chemical properties of MOFs are indeed predictable (stochastically, not deterministically) using machine learning methods and automated analysis protocols, with the accuracy of predictions increasing with sample size. Our initial results indicate that this methodology is promising to apply not only to gas storage in MOFs but in many other material science projects.
Editorial Summary
Machine learning: Quickly screening materials for effective gas storage(机器学习:快速筛选有效储气材料)
基于本研究结果,现在可以通过人工智能快速而准确地预测具有气体储存性能的金属-有机框架材料(MOF)。来自美国克里特大学的Froudakis开发了一种机器学习方法,以根据化学结构预测具有吸附H2/CO2性能的多孔MOF材料,有望应用于催化和气体储存。之前此类方法要么太慢,要么不够精确。本研究中,Froudakis等通过已知特性来训练该机器学习方法识别MOF中的某些结构特征,从而将“化学直觉”编入其算法中。然后,他们将该方法应用于新的MOF的大规模筛选,通过测试发现,所作的几个预测与实验数据相匹配。通过这种技术,有望更快地发现用于二氧化碳封存或氢气储存的新材料。
The gas storage properties of metal-organic frameworks can now be quickly and accurately predicted by artificial intelligence. George Froudakis at the University of Crete has developed a machine learning approach to predict the H2/CO2 adsorption properties of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), highly porous materials promising for catalysis and gas storage, based on their chemical structure. Previous methods were either too slow, or not accurate enough.Here, Froudakis and his team encoded ‘chemical intuition’ into their algorithm by training it to recognize certain structural features in MOFs with known properties. Then, when they applied the method to large-scale screening tests of new MOFs they found their predictions matched with experimental data. With this technique, it is hoped that new materials for CO2 sequestration or hydrogen storage will be discovered more quickly.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号