 An efficient and accurate framework for calculating lattice thermal conductivity of solids: AFLOW—AAPL Automatic Anharmonic Phonon Library (用于计算固体晶格热导率的准确有效框架:AFLOW-AAPL自动非谐波声子库)
An efficient and accurate framework for calculating lattice thermal conductivity of solids: AFLOW—AAPL Automatic Anharmonic Phonon Library (用于计算固体晶格热导率的准确有效框架:AFLOW-AAPL自动非谐波声子库)
Jose J. Plata, Pinku Nath, Demet Usanmaz, Jesús Carrete, Cormac Toher, Maarten de Jong, Mark Asta, Marco Fornari, Marco Buongiorno Nardelli & Stefano Curtarolo
npj Computational Materials 3:45 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0046-7
Published online:20 October 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
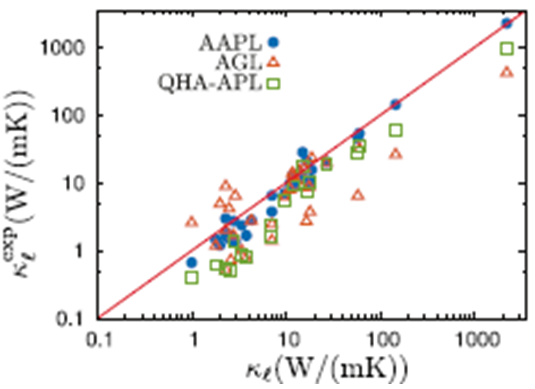
摘要:用于计算晶格热导率Kl的最准确方法之一,就是从三阶非谐力常数开始求解玻尔兹曼传输方程。除了第一原理参数化的基本近似之外,与此方法相关的两个主要挑战是:高昂的计算成本和框架的自动化不足,二者共同制约着具有特殊性能的新型材料的发现。为此,本研究提出了自动非谐波声子库(AAPL)方法。该方法通过有效利用晶体对称性分析,高效地计算原子力常数,解出玻尔兹曼传输方程获得Kl,并可以在用户最小程度干涉下完成完全一体化运算,从而成为当前高通量地加速材料开发框架AFLOW.的有效补充。该方法彰显了“实验与理论”相结合的研究方法,可以与其他软件包的精度和速度相比较,以及对强电子局域和关联的体系一样适用。将AAPL与伪杂化泛函ACBN0混合使用,可以在不增加计算需求量的前提下,提高计算精度。
Abstract:One of the most accurate approaches for calculating lattice thermal conductivity,κl, is solving the Boltzmann transport equation starting from third-order anharmonic force constants. In addition to the underlying approximations of ab-initio parameterization, two main challenges are associated with this path: high computational costs and lack ofautomation in the frameworks using this methodology, which affect the discovery rate of novel materials with ad-hoc properties.Here, the Automatic Anharmonic Phonon Library (AAPL) is presented.It efficiently computes interatomic force constants by making effective use of crystal symmetry analysis, it solves the Boltzmann transport equation to obtainκl, and allows a fully integrated operation with minimum user intervention, a rational addition to the current high-throughput accelerated materials development framework AFLOW.An “experiment vs. theory” study of the approach is shown, comparing accuracy and speed with respect to other available packages, and for materials characterized by strong electron localization and correlation.Combining AAPL with the pseudo-hybrid functional ACBN0 is possible to improve accuracy without increasing computational requirements.
Editorial Summary
Thermal conductivity: Framework for calculating heat flow in solids (导热系数:用于计算固体中热流的框架)
一种新理论框架可以为材料热导率的计算提供更加有效的方法。对于从散热片到隔热层的各种应用来说,了解材料如何传导热量非常重要。虽然热量如何在材料中传导具有基础性重要意义,但用其来预测一种材料的晶格导热性仍具挑战,并且一般还需要在该过程中输入具体特性的实验数据或理论知识。现在,来自杜克大学的Stefano Curtarolo领导的国际研究团队提出了一个框架,可以仅需单一输入文件而无需进一步干预,便可预测单晶和多晶材料的晶格热导率。该方法被称为自动非谐波声子库,使用对称性分析来计算某些参数,然后解出Boltzmann传输方程,提供有关电子结构和声子相关属性的信息。
A new theoretical framework could provide a more efficient method for calculating a material’s thermal conductivity. Understanding how materials conduct heat is crucial for a range of applications, from heat sinks to thermal insulation. Despite its fundamental importance, predicting a material’s lattice thermal conductivity is challenging, and often requires experimental data or knowledge of specific properties to be entered during the process. An international team of researchers led by Stefano Curtarolo from Duke University now present a framework that can predict the lattice thermal conductivity of single-crystal and polycrystalline materials using just a single input file, with no further intervention. Called the Automatic Anharmonic Phonon Library, the methods computes certain parameters using symmetry analysis, before solving the Boltzmann transport equation, providing information on both the electronic structure and phonon-dependent properties.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号