 Statistical variances of diffusional properties from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations (从头算分子动力学模拟的扩散特性的统计方差)
Statistical variances of diffusional properties from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations (从头算分子动力学模拟的扩散特性的统计方差)
Xingfeng He, Yizhou Zhu, Alexander Epstein & Yifei Mo
npj Computational Materials 4:18 (2018)
doi:10.1038/s41524-018-0074-y
Published online:03 April 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
摘要:从头算分子动力学(AIMD)模拟可以广泛用于研究材料的扩散机制和量化相应的材料扩散特性。然而,AIMD模拟通常局限在几百个原子的系统,且模拟时间也仅限于亚纳秒物理时域的范围,因此仅能涉及到有限的扩散几率,而无法描述其它扩散过程。这样致使AIMD模拟的扩散结果还往往受到统计误差的影响。本研究重新审视了通过AIMD模拟估算扩散系数和离子电导率的过程,并建立了具有最小拟合误差程序。此外,我们提出了相应的方法,能通过AIMD模拟到的扩散事目,来量化扩散系数和离子电导率的统计方差。由于扩散几率的采样必须达到足够的数目,因此AIMD模拟时间应足够长,而且只能在具有快速扩散的材料上进行研究。我们界定了应用AIMD模拟研究扩散特性所适用的材料范围和物理条件。本研究为量化AIMD模拟扩散结果的统计置信度以及正确应用这一强大技术奠定了基础。
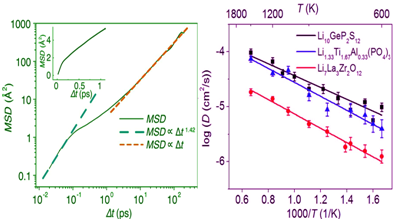
Abstract:Ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulation is widely employed in studying diffusion mechanisms and in quantifying diffusional properties of materials. However, AIMD simulations are often limited to a few hundred atoms and a short, sub-nanosecond physical timescale, which leads to models that include only a limited number of diffusion events.As a result, the diffusional properties obtained from AIMD simulations are often plagued by poor statistics.In this paper, we re-examine the process to estimate diffusivity and ionic conductivity from the AIMD simulations and establish the procedure to minimize the fitting errors.In addition, we propose methods for quantifying the statistical variance of the diffusivity and ionic conductivity from the number of diffusion events observed during the AIMD simulation.Since an adequate number of diffusion events must be sampled, AIMD simulations should be sufficiently long and can only be performed on materials with reasonably fast diffusion.We chart the ranges of materials and physical conditions that can be accessible by AIMD simulations in studying diffusional properties.Our work provides the foundation for quantifying the statistical confidence levels of diffusion results from AIMD simulations and for correctly employing this powerful technique.
Editorial Summary
Ionic diffusion: Mapping the uncertainty (离子扩散:描述不确定性)
通过从头算分子动力学模拟计算离子扩散系数,往往受到统计误差的影响,且无法保证其结果的准确度。受限于目前的计算能力,该模拟方法只能为小型系统和短时尺度进行建模,这在一定程度上限制了扩散记录的采样数量。来自马里兰大学的莫一非教授等介绍了获得离子扩散系数的一种最佳方法,并给出了该方法下的统计误差。研究结果显示,扩散系数的线性行为只发生在模拟时间的中间时段,且扩散系数的方差与所有离子的总均方位移相关,随着位移的增加,统计误差逐渐降低。他们发现,精确的离子扩散计算只能用于超离子导体或高温下的离子扩散,而无法保证其它材料扩散系数的估算的可靠性。
The calculation of ionic diffusivity with ab initio molecular dynamics is often plagued by poor statistics; how accurate are the results? Due to computational limits only small systems and timescales can be modeled, limiting the number of diffusion events sampled.Here, Yifei Mo and colleagues at the University of Maryland outline best practice to obtain ionic diffusivity, as well as how to obtain statistical errors with this approach.They show linear behavior in diffusivity only happens for intermediate time intervals of the simulations.Moreover, variance of diffusivity is related to the total mean squared displacement of all ions, the statistical error reducing as the displacement increases. Accurate ionic diffusion calculations can only be performed for super-ionic conductors, or at high temperature, with implications for the reliability of calculations of diffusivity in other materials.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号