 Computational design of bimetallic core-shell nanoparticles for hot-carrier photocatalysis(双金属核壳纳米粒子的热载流子光催化计算设计)
Computational design of bimetallic core-shell nanoparticles for hot-carrier photocatalysis(双金属核壳纳米粒子的热载流子光催化计算设计)
Luigi Ranno, Stefano Dal Forno & Johannes Lischner
npj Computational Materials 4:31 (2018)
doi:s41524-018-0088-5
Published online:06 july 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
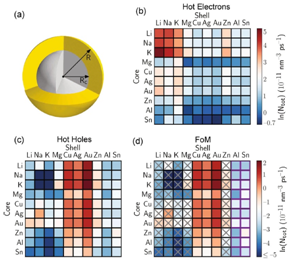
摘要:计算设计可以促进具有定制特性的新材料发现,但要将这种方法应用于直径大于几纳米的等离子体纳米颗粒,却很有挑战,因为原子级第一性原理计算不适用于这样的系统。本研究采用最近开发的材料特定方法进行计算,结合了电子有效质量理论和局部表面等离子体的准静态描述,可识别有望用于热电子光催化的双金属核-壳纳米颗粒。具体而言,我们计算了100种不同核壳纳米粒子的热载流子产生速率,发现具有碱金属核和过渡金属壳的材料系统,对水分子有强裂解性,且在水环境中有强稳定性。分析表明,这些系统的高效率与它们的电子结构有关,而电子结构在壳体中具有二维电子气。我们的计算还进一步证明了热载流子特性具有高度可调性,可用核心和壳体的尺寸进行灵敏的调控。从本研究得出的材料设计规律可用来指导改进太阳能转换装置。
Abstract:Computational design can accelerate the discovery of new materials with tailored properties, but applying this approach to plasmonic nanoparticles with diameters larger than a few nanometers is challenging as atomistic first-principles calculations are not feasible for such systems. In this paper, we employ a recently developed material-specific approach that combines effective mass theory for electrons with a quasistatic description of the localized surface plasmon to identify promising bimetallic core-shell nanoparticles for hot-electron photocatalysis.Specifically, we calculate hot-carrier generation rates of 100 different core-shell nanoparticles and find that systems with an alkali-metal core and a transition-metal shell exhibit high figures of merit for water splitting and are stable in aqueous environments.Our analysis reveals that the high efficiency of these systems is related to their electronic structure, which features a two-dimensional electron gas in the shell.Our calculations further demonstrate that hot-carrier properties are highly tunable and depend sensitively on core and shell sizes.The design rules resulting from our work can guide experimental progress towards improved solar energy conversion devices.
Editorial Summary
Photocatalysis: hot-carrier generation in bimetallic core-shell nanoparticles (光催化:双金属核壳纳米粒子中的热载流子生成)
对各种核-壳纳米粒子的计算筛选揭示,双金属系统是裂解水的理想选择。英国伦敦帝国理工学院的Luigi Ranno教授等进行了一项理论研究,将电子的有效质量理论与局部表面等离子体的准静态描述相结合。该方法可以计算来自数百个核-壳纳米颗粒的热载流子产生速率,并确定核-壳纳米颗粒是光催化应用的最佳候选物,能在水环境中保持稳定,满足了有效裂解水的关键要求。发现根据核和壳的尺寸在宽泛的范围内可对热载流子性质进行调节。值得注意的是,具有碱金属核和过渡金属壳的双金属纳米颗粒,在增强的热载流子产生速率和水分解能力方面,提供了最高的品质因数。
A computational screening of a variety of core-shell nanoparticles unveil that bimetallic systems are ideal for water splitting. A team led by Luigi Ranno at Imperial College London performed a theoretical study combining effective mass theory for electrons with a quasistatic description of localized surface plasmons.This approach allowed to compute the rates of hot-carrier generation from hundreds of core-shell nanoparticles, and to identify the optimal candidates for photocatalysis applications that are stable in aqueous environment, the latter being a crucial requirement for effective water splitting.The hot-carrier properties were found to be broadly tunable as a function of the core and shell sizes.Notably, bimetallic nanoparticles with an alkali-metal core and a transition-metal shell were found to provide the highest figures of merit in terms of enhanced hot-carrier generation rates and water splitting ability.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号