 Entropy contributions to phase stability in binary random solid solutions (熵对二元随机固溶体相稳定性的贡献)
Entropy contributions to phase stability in binary random solid solutions (熵对二元随机固溶体相稳定性的贡献)
Anus Manzoor, Shubham Pandey, Debajit Chakraborty, Simon R. Phillpot & Dilpuneet S. Aidhy
npj Computational Materials 4:47 (2018)
doi:s41524-018-0102-y
Published online:22 August 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
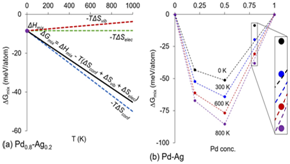
摘要:高熵合金含有多种元素而且比例很大,容易导致相分离。这些合金通常具有浅混合焓,导致了相似级别的熵贡献。因此,合金的相稳定性平等地取决于混合焓和混合熵,了解二者各自对热力学性质的贡献就成为关键。在设计高熵合金的总体框架中,本研究使用密度泛函理论计算,阐明了振动熵、电子熵和位形熵对二元合金相稳定性的贡献。研究表明,与振动熵和位形熵相比,电子熵的贡献非常小,并且在合金的相稳定性中不起重要作用。位形熵和振动熵既能破坏固溶体的稳定又可共助固溶体的稳定。因此,即使那些具有负混合焓的系统也可能表现出相不稳定性,呈现混溶带隙;相反,由于熵贡献,那些具有正混合焓的系统却可以是相稳定的。我们认为,与有序金属间化合物不同,综合考虑各种熵贡献,对于具有浅混合焓的稳定、单相高熵合金的计算预测理论框架的发展来说,非常重要。
Abstract:High entropy alloys contain multiple elements in large proportions that make them prone to phase separation.These alloys generally have shallow enthalpy of mixing which makes the entropy contributions of similar magnitude. As a result, the phase stability of these alloys is equally dependent on enthalpy and entropy of mixing and understanding the individual contribution of thermodynamic properties is critical. In the overall vision of designing high entropy alloys, in this work, using density functional theory calculations, we elucidate the contributions of various entropies, i.e., vibrational, electronic and configurational towards the phase stability of binary alloys. We show that the contribution of electronic entropy is very small compared to the vibrational and configurational entropies, and does not play a significant role in the phase stability of alloys. The configurational and vibrational entropies can either destabilize or can collectively contribute to stabilize the solid solutions. As a result, even those systems that have negative mixing enthalpy can show phase instability, revealed as a miscibility gap; conversely, systems with positive mixing enthalpy can be phase stable due to entropic contributions. We suggest that including entropic contributions are critical in the development of theoretical framework for the computational prediction of stable, single-phase high entropy alloys that have shallow mixing enthalpies, unlike ordered intermetallics.
Editorial Summary
Phase stability: entropy enabled predictions (相稳定性:启用熵来预测)
位形熵和振动熵虽然一直以来被忽视,但现在本研究指出,二者可能确定了合金的相稳定性。来自美国怀俄明大学的DilpuneetAidhy教授等,采用密度泛函理论计算,检验了不同类型的熵在7种具有浅混合焓的二元金属合金中的贡献。他们发现依靠混合焓来预测固溶体稳定性是不够的。虽然电子熵对任何合金的相稳定性没有显著贡献,但是位形熵稳定了固溶体,同时振动熵在不同合金系统中起促进或破坏固溶体稳定的作用。振动熵是衡量原子键柔软度的指标,研究它在不同体系中的变化方式,可能有助于我们更好地预测单相多组分合金的稳定性。
Configurational and vibrational entropies, while conventionally neglected, can determine an alloy’s phase stability. A team led by DilpuneetAidhy at the University of Wyoming in U.S.A. used density functional theory calculations to examine the contribution of different types of entropy in seven binary metallic alloys with shallow enthalpies of mixing. They found that relying on the enthalpy of mixing to predict solid solution stability was insufficient. While electronic entropy did not meaningfully contribute to phase stability in any of the alloys, configurational entropy stabilized solid solutions, while vibrational entropy either stabilized or destabilized solid solutions depending on the alloy system. Vibrational entropy is a measure of the softness of atomic bonds, and research into how it varies in different systems may help us better predict single-phase multicomponent alloy stability.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号