 Empirical modeling of dopability in diamond-like semiconductors (类金刚石半导体掺杂性能的经验模型)
Empirical modeling of dopability in diamond-like semiconductors (类金刚石半导体掺杂性能的经验模型)
Samuel A. Miller, Maxwell Dylla, Shashwat Anand, Kiarash Gordiz, G. Jeffrey Snyder & Eric S. Toberer
npj Computational Materials 4:71 (2018)
doi:s41524-018-0123-6
Published online:06 December 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
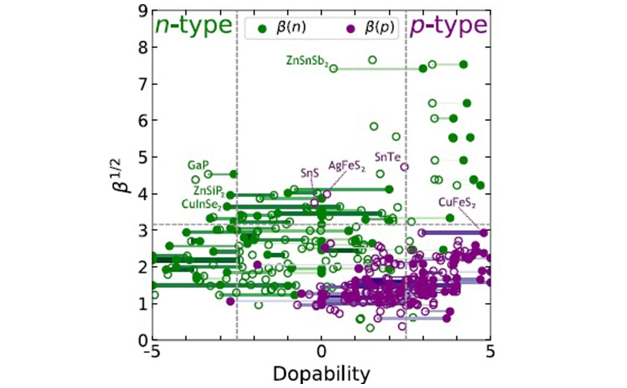
摘要:载流子浓度的优化在新型半导体的开发应用中(应用于诸如热电、透明导体和光伏等)一直是个挑战。这个问题在高通量的材料性能预测中尤其严重,由于计算量巨大,载流子浓度通常只能被假定为自由参数,其掺杂极限无法预测。本研究探索了机器学习在高通量预测载流子浓度方面的应用。我们将模型限定在类金刚石半导体材料体系中,基于从一元到四元共计127种化合物载流子浓度的实验数据,开发了机器学习数据集。采用各种统计和机器学习方法对这些数据进行分析。进而准确预测了类金刚石半导体材料的掺杂性能,预测的载流子浓度,不论对于p型还是n型,与实验值偏差都在一个数量级以内。通过分析拟合的模型,我们揭示了载流子浓度变化的趋势,并且与之前的计算工作进行了比较。最后,我们将该模型掺杂性能预测与高通量的品质因子预测相结合,预测了新型的热电材料。
Abstract:Carrier concentration optimization has been an enduring challenge when developing newly discovered semiconductors for applications (e.g., thermoelectrics, transparent conductors, photovoltaics). This barrier has been particularly pernicious in the realm of high-throughput property prediction, where the carrier concentration is often assumed to be a free parameter and the limits are not predicted due to the high computational cost. In this work, we explore the application of machine learning for high-throughput carrier concentration range prediction. Bounding the model within diamond-like semiconductors, the learning set was developed from experimental carrier concentration data on 127 compounds ranging from unary to quaternary. The data were analyzed using various statistical and machine learning methods. Accurate predictions of carrier concentration ranges in diamond-like semiconductors are made within approximately one order of magnitude on average across both p- and n-type dopability. The model fit to empirical data is analyzed to understand what drives trends in carrier concentration and compared with previous computational efforts. Finally, dopability predictions from this model are combined with high-throughput quality factor predictions to identify promising thermoelectric materials.
Editorial Summary
THERMOELECTRICS: Looking back is looking forward (热电材料:回首过去即是展望未来)
实验测量的载流子浓度是理解和预测高性能热电材料的模型基础。载流子浓度对于控制材料性能十分重要。尽管实验已经取得了极大的进展,但建立掺杂性能的预测准则来实现材料性能设计仍是一种挑战。来自美国西北大学、科罗拉多矿业学院和美国国家可再生能源实验室的研究团队,根据实验报道的127种化合物的掺杂限值数据,预测了部分类金刚石半导体的掺杂范围,并筛选出了了几种兼具较高热电品质因子和较好掺杂性能的材料。该模型不仅阐明了类金刚石材料体系掺杂性能的决定因素,还预测了部分潜在的高性能热电化合物,这些材料值得后续研究关注。
Experimental carrier concentration can serve as the basis for a model to understand and predict high performance thermoelectrics. Carrier concentration is instrumental in controlling properties. Despite significant experimental progress, establishing guidelines towards the desired performance through doping remains challenging. Now, a team from Northwestern University, Colorado School of Mines, and National Renewable Energy Laboratory in USA have predicted the dopability ranges of several diamond-like semiconductors, based on data from experimentally reported doping limits for 127 compounds. Several materials that combine simultaneously promising thermoelectric quality factor and complementary dopability are singled out. Apart from shedding light on what drives dopability in this family, the model also suggests that a number of less-studied compounds deserve more attention.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号