 Local-environment dependence of stacking fault energies in concentrated solid-solution alloys(高浓度固溶体合金中堆垛层错能的局域环境依赖性)
Local-environment dependence of stacking fault energies in concentrated solid-solution alloys(高浓度固溶体合金中堆垛层错能的局域环境依赖性)
Shijun Zhao, Yuri Osetsky, G. Malcolm Stocks & Yanwen Zhang
npj Computational Materials 5:13 (2019)
doi:s41524-019-0150-y
Published online:04 February 2019
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
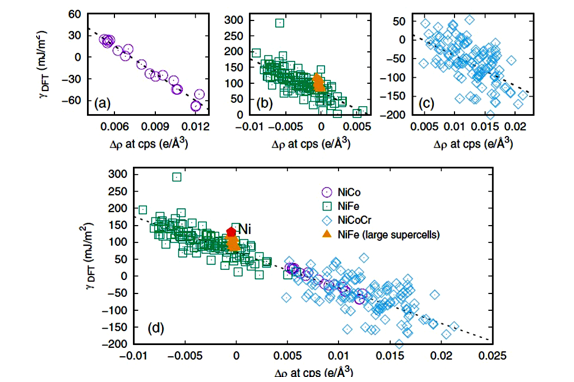
摘要:基于3d过渡金属的高浓度固溶体合金(CSA)拥有非凡的机械性能和抗辐照性能,这些优异的性能都与其较低的堆垛层错能(SFE)相关。由于内在的无序原子排布,CSA中的SFE值取决于局部原子的空间分布。本研究基于经验势和第一原理计算,研究了NiCo、NiFe和NiCoCr的等高浓度CSA中SFE的分布。我们的研究表明,无序结构的CSA中SFE的分布取决于计算中采用的堆垛层错区域的大小。通过电子结构分析,我们发现CSA中SFE的变化与堆垛层错区域中的电荷密度再分布有关。我们进一步提出了一个化学键断裂和再形成的模型来描述这种局部SFE的变化,从而可以基于局部结构来研究和预测CSA中的SFE的分布。我们的结果还表明,对于NiCo,堆垛层错引起的扰动仅局限于层错附近的最近邻密排面,而在NiFe和NiCoCr中,由于Fe和Cr的部分填充的d电子的存在,层错的扰动可以延伸到第三近邻的密排面。
Abstract:Concentrated solid-solution alloys (CSAs) based on 3d transition metals have demonstrated extraordinary mechanical properties and radiation resistance associated with their low stacking fault energies (SFEs). Owing to the intrinsic disorder, SFEs in CSAs exhibit distributions depending on local atomic configurations. In this work, the distribution of SFEs in equiatomic CSAs of NiCo, NiFe, and NiCoCr are investigated based on empirical potential and first-principles calculations. We show that the calculated distribution of SFEs in chemically disordered CSAs depends on the stacking fault area using empirical potential calculations. Based on electronic structure calculations, we find that local variations of SFEs in CSAs correlate with the charge density redistribution in the stacking fault region. We further propose a bond breaking and forming model to understand and predict the SFEs in CSAs based on the local structure alone. It is shown that the perturbation induced by a stacking fault is localized in the first-nearest planes for NiCo, but extends up to the third nearest planes for NiFe and NiCoCr because of partially filled d electrons in Fe and Cr.
Editorial Summary
Concentrated solid-solution alloys: stacking fault energy and its local environment dependence(高浓度固溶体合金:堆垛层错能与层错局部环境的关系)
该研究发现高浓度固溶合金中的堆垛层错能与堆垛层错所在区域的电荷密度再分布相关。来自美国橡树岭国家实验室的Shijun Zhao(赵仕俊,现为香港城市大学机械工程系助理教授)等人,基于经验势和第一原理计算,研究了NiCo、NiFe和NiCoCr的等高浓度固溶合金中堆垛层错能的分布。他们发现堆垛层错的影响在NiCo中是局部的,而在NiFe和NiCoCr中是相对长程的,证明了高浓度固溶体合金中的局部堆垛层错能可以用化学键临界点处的电荷密度再分布来表征,并进一步提出了一个化学键的断裂和再形成模型。依据该模型仅凭短程效应即可预测特定原子空间构型下的局部堆垛层错能,并可表征堆垛层错能对局部环境的依赖性。这些研究结果使局部原子空间排列及其堆垛层错能之间建立了明确的联系,对理解高浓度固溶体合金的局部性质和预测相关效应(如材料相和结构稳定性、原子转移、位错性质等)都非常重要。
Stacking fault energy (SFE) in concentrated solid-solution alloys (CSAs) is related to charge density redistribution in the region where stacking faults are located. A team from Oak Ridge National Laboratory, studied the SFE distribution of NiCo, NiFe and NiCoCr CSAs based on empirical and first-principles calculations. They found that the effect of stacking faults is localized in NiCo and relatively long-ranged in NiFe and NiCoCr, demonstrating that the local SFE can be described by charge density redistribution at the bond critical points. Based on electronic structure results, they further proposed a bond breaking and formation model to understand the SFE distributions in CSAs, by which the short-range effect can be used to predict the local SFE under a specific atomic configuration. These findings establish a clear link between local atomic configuration and SFE, which are important for understanding the local properties of CSAs and predicting the associated effects.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号