 Comparison of dissimilarity measures for cluster analysis of X-ray diffraction data from combinatorial libraries (组合数据库中X射线衍射数据对团簇分析的不同方法比较)
Comparison of dissimilarity measures for cluster analysis of X-ray diffraction data from combinatorial libraries (组合数据库中X射线衍射数据对团簇分析的不同方法比较)
Yuma Iwasaki, A. Gilad Kusne & Ichiro Takeuchi
npj Computational Materials 3, Article number: 4 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0006-2
Published online:03 February 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
摘要:机器学习技术已被证明在管理全方位不断增长的材料研究数据量方面,拥有难以估量的作用,包括管理不断增长的高通量材料模拟、制造和表征所产生的数据。尤其是机器学习技术已被证明可用于快速自动识别材料组成、结构数据库中潜在新材料的元素组成–相图,能使人们快速进行新材料的制备-结构-性能一体化分析及功能材料的发现。自动相图测定方法改进的一个关键问题是,选择不同措施或软件核心功能。所选的措施要能减少复杂结构数据问题对性能分析的影响。该关键问题包括,某个材料的晶格常数改变后,峰高的变化和峰值的移位。在本研究中,我们考察了基于X-射线衍射的结构分析方法以及不同方法对相组成描绘结果的差异。本研究分析了Fe–Co–Ni三元合金成分扩散状态的X-射线衍射结果,比较了9种不同方法对结果的影响。采用余弦、Pearson相关系数和Jensen–Shannon发散方法,在未知峰值位移幅度的情况下,得出了峰高变化和峰值移位(由于晶格常数的改变)时的最佳结果。随着已知的最大峰值移位,动态时间扭曲的归一化约束模式提供了最好的结果。本研究结果也可作为快速分析大量X射线衍射结果(超出组合库数据)的通用策略。
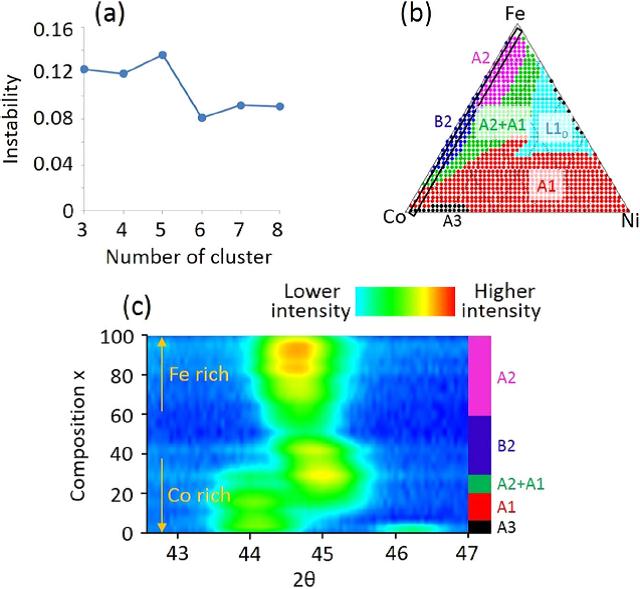
Abstract: Machine learning techniques have proven invaluable to manage the ever growing volume of materials research data produced as developments continue in high-throughput materials simulation, fabrication, and characterization. In particular, machine learning techniques have been demonstrated for their utility in rapidly and automatically identifying potential composition–phase maps from structural data characterization of composition spread libraries, enabling rapid materials fabrication-structure-property analysis and functional materials discovery. A key issue in development of an automated phase-diagram determination method is the choice of dissimilarity measure, or kernel function. The desired measure reduces the impact of confounding structural data issues on analysis performance. The issues include peak height changes and peak shifting due to lattice constant change as a function of composition. In this work, we investigate the choice of dissimilarity measure in X-ray diffraction-based structure analysis and the choice of measure’s performance impact on automatic composition-phase map determination. Nine dissimilarity measures are investigated for their impact in analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns for a Fe–Co–Ni ternary alloy composition spread. The cosine, Pearson correlation coefficient, and Jensen–Shannon divergence measures are shown to provide the best performance in the presence of peak height change and peak shifting (due to lattice constant change) when the magnitude of peak shifting is unknown. With prior knowledge of the maximum peak shifting, dynamic time warping in a normalized constrained mode provides the best performance. This work also serves to demonstrate a strategy for rapid analysis of a large number of X-ray diffraction patterns in general beyond data from combinatorial libraries.
Editorial Summary
Machine learning: Spying enhanced materials with x-ray vision (机器学习技术:增强X射线的视力以更好地窥探材料)
来自美国国家标准局的A. Gilad Kusne及其同事通过不同措施,量化材料结构的关键数据(如X-射线衍射峰强度和位置,以及样品的组成变化),研究了机器学习技术,以使其能够简化新型合金的合成。利用大量X射线衍射数据集的自动变化计算,可以改善多组分合金的设计。合金中含三个或更多金属时,有可能出现大量不同组合的材料,每种材料都具有不同的性能。科学家们首先制备了成分扩散的铁-钴-镍合金薄膜,然后用不同软件分析X射线的异同,评估处理的速度和准确性。研究鉴定了几种适用于高通量生成彩色编码图样的算法,这些算法能显示合金成分和相位在两个和三个维度之间的关系。
Using algorithms to automatically spot variations in massive X-ray diffraction data sets may improve design of multi-component alloys. Having three or more metals in an alloy can lead to overwhelming combinations of possible materials, each with different properties. A. Gilad Kusne from the National Institute of Standards and co-workers examined how machine learning techniques could simplify alloy discovery through ‘dissimilarity measures’ that quantify how key structural data points, such as the positions and intensities of X-ray peaks, change with sample makeup.
The team fabricated a compositional spread of iron–cobalt–nickel thin film alloys, and then evaluated different software approaches to finding X-ray dissimilarities for both processing speed and accuracy. Several algorithms suitable for high-throughput generation of color-coded maps that display relations between alloy composition and phase in both two and three-dimensions were identified. 

 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号