 Nanomaterials: A semiconductor with an enhanced signature(新型半导体纳米材料,让待检分子的拉曼信号放大)
Nanomaterials: A semiconductor with an enhanced signature(新型半导体纳米材料,让待检分子的拉曼信号放大)
Yufeng Shan, Zhihui Zheng, Jianjun Liu, Yong Yang, Zhiyuan Li, Zhengren Huang & Dongliang Jiang
npj Computational Materials 3, Article number: 11 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0008-0
Published online:15 March 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
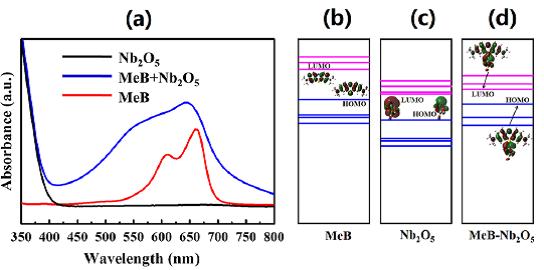
摘要:表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)是一种强大的高灵敏分析技术,它可以探测和分析物质表层所吸附的分子数量。目前仅限少数几种贵金属纳米结构能够产生如此强度的SERS效应,极大地限制了这一技术的应用。半导体SERS材料可以克服贵金属衬底的一些缺点,有望使得SERS技术在表面科学、光谱和生物医药领域得到进一步应用;但是其探测灵敏度及信号增强效果均受制于半导体衬底较弱的SERS活性。本研究报道了一种新型半导体SERS活性衬底材料Nb2O5,可以高灵敏度地检测染料分子。其在633和780nm激光激发下,探测亚甲基蓝染料的SERS增强因子高达107以上,是目前发现的灵敏度最高的半导体衬底材料,甚至可以和具有“热点效应”的金属纳米结构衬底相媲美。通过密度泛函理论和有限元计算表明,Nb2O5如此之高的SERS活性可以归因于光诱导电荷转移的化学增强机制和电磁场增强机制的叠加作用。在分子Nb2O5体系中,Nb2O5和表面吸附的染料分子,共同产生了新的分子最高占据轨道和最低未占据轨道,因此在长波长的激发光下,电子仍能够轻易跃迁。除此之外,电磁增强也为增强因子贡献了两个数量级。本研究表明,Nb2O5纳米粒子有望作为一种新型半导体SERS材料,取代贵金属,在生物相关领域发挥其巨大应用潜力。
Abstract: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering technique, as a powerful tool to identify the molecular species, has been severely restricted to the noble metals. The surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on semiconductors would overcome the shortcomings of metal substrates and promote development of surface-enhanced Raman scattering technique in surface science, spectroscopy, and biomedicine studies. However, the detection sensitivity and enhancement effects of semiconductor substrates are suffering from their weak activities. In this work, a semiconductor based on Nb2O5 is reported as a new candidate for highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of dye molecules. The largest enhancement factor value greater than 107 was observed with the laser excitation at 633 and 780 nm for methylene blue detection. As far as literature review shows, this is in the rank of the highest sensitivity among semiconductor materials; even comparable to the metal nanostructure substrates with “hot spots”. The impressive surface-enhanced Raman scattering activities can be attributed to the chemical enhancement dominated by the photo-induced charge transfer, as well as the electromagnetic enhancement, which have been supported by the density-functional-theory and finite element method calculation results. The chemisorption of dye on Nb2O5 creates a new highest occupied molecular orbital and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital contributed by both fragments in the molecule-Nb2O5 system, which makes the charge transfer more feasible with longer excitation wavelength. In addition, the electromagnetic enhancement mechanism also accounts for two orders of magnitude enhancement in the overall enhancement factor value. This work has revealed Nb2O5 nanoparticles as a new semiconductor surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate that is able to replace noble metals and shows great potentials applied in the fields of biology related.
Editorial Summary
中国科学家新近发现了一种能检测痕量生物小分子的新型半导体材料。来自中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所的杨勇、黄政仁等,发现Nb2O5可以显著增强生物医药领域染料分子的拉曼信号。粗糙衬底上的纳米尺寸效应能增加光场,利用这种增强的光信号来检测特定分子的技术叫表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)技术。但只有少数几种贵金属材料(如金、银)才能将信号强度提高到实用水平。杨勇等发现了一种目前SERS活性最强的半导体衬底材料,氧化铌纳米晶,可以高灵敏检测亚甲基蓝、甲基紫以及甲基蓝等染料分子。他们在检测亚甲基蓝染料时发现,在633和780 nm光激发下,拉曼信号增强了107倍以上。
A semiconductor that makes recognizing molecules easier is identified by researchers in China. Yong Yang and co-workers from the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics show that niobium pentoxide can strongly enhance the optical signature of the colored dyes used in biomedical applications. Nanometer-sized features on a rough surface can increase optical fields. This phenomenon can enhance the optical signature used to identify a specific molecule in a technique called surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS).But only a few materials, notably noble metals such as gold and silver, have demonstrated useful levels of enhancement. Yang et al. find that niobium pentoxide nanoparticles can be used as a most-active SERS semiconductor substrate to detect the dyes methylene blue, methyl violet and methyl blue. They measured a SERS enhancement factor of over ten million using 633 and 780 nano meter light to detect methylene blue.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号