 Phonon broadening in high entropy alloys(高熵合金中的声子宽频化)
Phonon broadening in high entropy alloys(高熵合金中的声子宽频化)
Fritz Körmann, Yuji Ikeda, Blazej Grabowski & Marcel H. F. Sluiter
npj Computational Materials 3:36 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0037-8
Published online:01 September 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
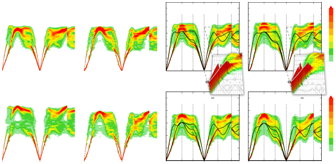
摘要:耐火高熵合金具有突出的特性,有望成为下一代用于高温环境的材料。高温中,晶格振动(声子)将强烈影响材料的性质。声子对材料性能的影响主要体现在热力学稳定性、热力学函数、弹性性能和热导率。与完美晶体和有序合金相比,多组分无规合金(高熵合金)中固有的质量和力常数涨落可引起显著的声子散射和声子频率的宽化。尽管这一现象很重要,但迄今为止对高熵合金中的声子散射和声子宽频化还少有研究。本研究从理论的角度试图解决这个挑战,采用第一原理计算来系统地研究质量和力常数涨落对12个具有体心立方结构的随机合金的声子谱的影响。这些结构包含二元合金到五组分的高熵合金,并探讨合金化学组分的复杂性如何影响材料的晶格振动行为。研究发现,质量和力常数涨落对声子的影响都需考虑,缺一不可。若忽略其中任何一项,物理图像将出现明显错误,如声子带隙的错误估算。本研究分析了声子行为如何影响宏观热力学量,尤其是振动熵。随着合金中元素种类的增加,振动熵也相应变大,其变化可能与构型熵的变化一样大,并严重影响材料的相稳定性。本研究结果基于以下合金:MoTa、MoTaNb、MoTaNbW、MoTaNbWV、VW、VWNb、VWTa、VWNbTa、VTaNbTi、VWNbTaTi、HfZrNb和HfMoTaTiZr。
Abstract: Refractory high entropy alloys feature outstanding properties making them a promising materials class for next-generation high-temperature applications. At high temperatures, materials properties are strongly affected by lattice vibrations (phonons). Phonons critically influence thermal stability, thermodynamic and elastic properties, as well as thermal conductivity. In contrast to perfect crystals and ordered alloys, the inherently present mass and force constant fluctuations in multi-component random alloys (high entropy alloys) can induce significant phonon scattering and broadening. Despite their importance, phonon scattering and broadening have so far only scarcely been investigated for high entropy alloys. We tackle this challenge from a theoretical perspective and employ ab initio calculations to systematically study the impact of force constant and mass fluctuations on the phonon spectral functions of 12 body-centered cubic random alloys, from binaries up to 5-component high entropy alloys, addressing the key question of how chemical complexity impacts phonons. We find that it is crucial to include both mass and force constant fluctuations. If one or the other is neglected, qualitatively wrong results can be obtained such as artificial phonon band gaps. We analyze how the results obtained for the phonons translate into thermodynamically integrated quantities, specifically the vibrational entropy. Changes in the vibrational entropy with increasing the number of elements can be as large as changes in the configurational entropy and are thus important for phase stability considerations. The set of studied alloys includes MoTa, MoTaNb, MoTaNbW, MoTaNbWV, VW, VWNb, VWTa, VWNbTa, VTaNbTi, VWNbTaTi, HfZrNb, HfMoTaTiZr.
Editorial Summary
High entropy alloys: Theoretical perspectives on phonons(高熵合金:声子的理论研究)
与传统合金相比,高熵合金在单个“晶格”内具有五种甚至更多种元素的同数量原子,并表现出一些非凡的物理性质。所有这些性质都受晶格振动(即声子)的影响,彰显了构造声子激发和声子间相互作用模型的重要性。来自荷兰代尔夫特理工大学的FritzKörmann和来自日本京都大学的池田宇池博士等对12种不同的耐火合金进行了第一性原理的计算,以解决合金化学组分的复杂性如何影响材料的晶格振动行为。结果表明,原子质量和力常数二者都可影响声子频率,并且在元素较多的合金中,其振动熵的变化幅度与构型熵的相当。这项基于理论计算角度的声子宽频化研究为高温高熵合金的设计开辟了道路。
In contrast to conventional alloys, high entropy alloys possess five or more equiatomic elemental species within a single lattice, resulting in some extraordinary physical properties. All these properties are linked to the lattice vibrations, i.e. phonons, indicating the importance of modelling of phonon excitations and their interactions. A team led by Fritz Körmann at Netherlands’ Delft University of Technology and Yuji Ikeda at Kyoto University in Japan performed first-principles calculations on 12 different refractory alloys to address the key question of how the chemical complexity impacts phonons. Results show that both atomic mass and force constants contribute to the phonon energies, and changes in the vibrational entropy with more elements could be comparable to the configurational entropy. Research into the computationally designed phonon broadening may open an avenue towards tailored high temperature high entropy alloys.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号