 Voltage-driven charge-mediated fast 180 degree magnetization switching in nanoheterostructure at room temperature (室温下纳米异质结构的快速180度磁化切换:电压驱动、电荷介导)
Voltage-driven charge-mediated fast 180 degree magnetization switching in nanoheterostructure at room temperature (室温下纳米异质结构的快速180度磁化切换:电压驱动、电荷介导)
Min Yi, Hongbin Zhang & Bai-Xiang Xu
npj Computational Materials 3:38 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0043-x
Published online:22 September 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
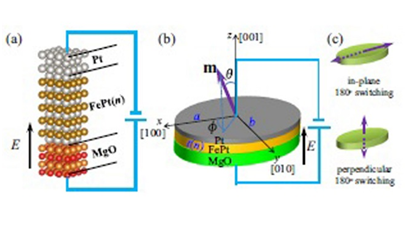
摘要:依赖电压而无需电流驱动的180°磁化切换为自旋电子学的革命提供了可能性。本研究通过第一性原理计算和有限温度下磁化动力学模拟相结合,模拟了室温下电压驱动的电荷介质180°磁化切换。发现电场(E)诱导的界面电荷可对纳米磁体的磁各向异性(K)有巨大的调制作用。特别地,K显示出相对于E和外延应变的线性变化。采用所获K的磁化动力学模拟表明,E脉冲可以实现平面和垂直方向180°的磁化切换。温度效应造成磁性180°切换很不稳定,其状态具有随机性。统计分析表明,通过控制E的大小和脉冲宽度,可以在室温下实现快速(约4 ns)和低误差率的180°切换。该研究为微型纳米级自旋电子器件的合理设计提供了启发,避免了热涨落对体系性能的较大影响。
Abstract: Voltage-driven 180° magnetization switching without electric current provides the possibility for revolutionizing the spintronics. We demonstrated the voltage-driven charge-mediated 180° magnetization switching at room temperature by combining first-principles calculations and temperature-dependent magnetization dynamics simulation. The electric field (E)-induced interface charge is found to allow a giant modulation of the magnetic anisotropy (K) of the nanomagnet. Particularly K is revealed to vary linearly with respect toE and the epitaxial strain. Magnetization dynamics simulations using the so-obtained K show that both in-plane and perpendicular 180° switching can be achieved by E pulses. The temperature effect renders the 180° switching as probability events. Statistical analysis indicates a fast (around 4 ns) and low-error-probability 180° switching achievable at room temperature by controlling the magnitude of E and the pulse width. The study inspires the rational design of miniaturized nanoscale spintronic devices where thermal fluctuation has a great impact.
Editorial Summary
Spintronics: simulations predict room temperature voltage-driven magnetization switching(自旋电子学:模拟预测室温电压驱动磁化切换)
计算模拟表明,电压诱导的界面电荷变化可导致Pt / FePt / MgO异质结在室温下的180°磁化切换。德国达姆施塔特技术大学的Min Yi、Hongbin Zhang和许旭祥,通过第一性原理计算和有限温度下磁化动力学模拟相结合,研究了横向尺寸为几十纳米的外延Pt / FePt / MgO异质结。发现电场在FePt / MgO界面处诱导电荷变化,并通过影响FePt层中的磁晶各向异性改变异质结的易磁化轴。通过调谐电场、外延应变和磁化动力学,在平面和垂直方向的平衡磁态下,可在室温下实现平面和垂直方向180°的磁化切换。这些结果为电压驱动磁性开关器件的设计提供了深入认识。
Simulations show that voltage-induced interfacial charge variation results in 180° magnetization switching at room temperature in a Pt/FePt/MgOheterostructure. Min Yi, Hongbin Zhang and Bai-Xiang Xu from TechnischeUniversität Darmstadt in Germany study an epitaxial Pt/FePt/MgOheterostructure with a lateral size of several tens of nanometers, by combining first-principles calculations and temperature-dependent magnetization dynamics simulations. The electric field induces charge variation at the FePt/MgO interface, which alters the magnetic easy axis of the heterostructure by affecting the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy in the FePt layer. By tuning the electric field, epitaxial strain and magnetization dynamics, in-plane and perpendicular 180° magnetization switching is achievable at room temperature in the case of in-plane and perpendicular equilibrium magnetic state, respectively. These results provide insight into the design of voltage-driven magnetic switching devices.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号