 The origin of uniaxial negative thermal expansion in layered perovskites(层状钙钛矿中单轴负热膨胀的起源)
The origin of uniaxial negative thermal expansion in layered perovskites(层状钙钛矿中单轴负热膨胀的起源)
Chris Ablitt, Sarah Craddock, Mark S. Senn, Arash A. Mostofi & Nicholas C. Bristowe
npj Computational Materials 3:44 (2017)
doi:10.1038/s41524-017-0040-0
Published online:16 October 2017
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
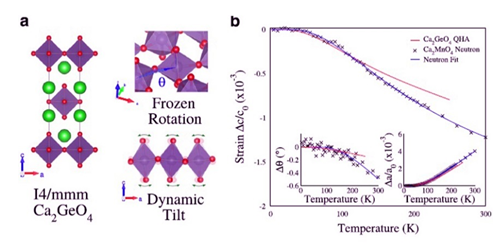
摘要:为什么ABO3钙钛矿在宽温度范围内通常不会呈现负热膨胀(NTE),而同一化学家族的层状钙钛矿却常常会发生?通常认为有两个关键因素决定了NTE的程度:1)存在驱动收缩的软声子模式(具有负的Grüneisen参数)和2)各向异性弹性柔量使材料易于沿着特定轴线作NTE所需的变形。考虑到ABO3和层状钙钛矿在其高对称相中通常具有等量的组分,热膨胀性能如此不同令人惊奇。采用第一原理计算和对称性分析,本研究显示,在分层钙钛矿中,八面体氧的分层和压缩旋转两个效应的组合,导致由对称破裂而引起的弹性各向异性显著增强。这一特征只存在于具有某种对称性的层状钙钛矿,它可以使层状钙钛矿在大的温度范围内保持单轴NTE。这一重要研究结果提示,对称性和弹性张量可以作为描述因子进行高通量筛选和引导材料设计。
Abstract:Why is it that ABO3 perovskites generally do not exhibit negative thermal expansion (NTE) over a wide temperature range, whereas layered perovskites of the same chemical family often do? It is generally accepted that there are two key ingredients that determine the extent of NTE: the presence of soft phonon modes that drive contraction (have negative Grüneisen parameters); and anisotropic elastic compliance that predisposes the material to the deformations required for NTE along a specific axis. This difference in thermal expansion properties is surprising since both ABO3 and layered perovskites often possess these ingredients in equal measure in their high-symmetry phases. Using first principles calculations and symmetry analysis, we show that in layered perovskites there is a significant enhancement of elastic anisotropy due to symmetry breaking that results from the combined effect of layering and condensed rotations of oxygen octahedra. This feature, unique to layered perovskites of certain symmetry, is what allows uniaxial NTE to persist over a large temperature range. This fundamental insight means that symmetry and the elastic tensor can be used as descriptors in high-throughput screening and to direct materials design.
Editorial Summary
Negative thermal expansion: symmetry controls the behavior of perovskites(负热膨胀:对称性控制着钙钛矿的行为)
对称破裂是层状钙钛矿单轴负热膨胀(NTE)的主要原因。来自英国帝国理工学院、华威大学和肯特大学的研究人员发现,是原子因素导致具有ABO3通式的钙钛矿氧化物材料,表现出与它们的层状对称物(称为Ruddlesden-Popper氧化物)极为不同的热膨胀性能。研究人员采用第一原理计算发现,层状钙钛矿中某些结构构型可能偏离完全对称的位置,而普通钙钛矿中结构构型被固定得更为牢固。层状钙钛矿中普遍存在的这种特征,允许单轴负热膨胀,即在很宽的温度范围内,随着温度升高,材料的收缩得以持续。这一基础的成果将有助于新型NTE材料的高通量筛选,并指引着未来的材料设计。
Symmetry breaking is a major cause of uniaxial negative thermal expansion (NTE) in layered perovskites. Researchers at Imperial College, the University of Warwick and the University of Kent have discovered the atomic factors causing perovskite oxides, materials with the general formula ABO3, to show very different thermal expansion properties from their layered counterparts, known as Ruddlesden-Popper oxides. Using first-principles calculations, the researchers found that in layered perovskites certain structural motifs can deviate from a perfectly symmetric arrangement, whereas in regular perovskites they are more firmly fixed. This feature, prevalent in layered perovskites, is what allows uniaxial negative thermal expansion, i.e., the contraction of the material with increased temperature, to persist over a large temperature range. This fundamental insight could aid high-throughput screening for new NTE materials and help direct future materials design.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号