 An effective method to screen sodium-based layered materials for sodium ion batteries (一种筛选钠离子电池钠基层状材料的有效方法)
An effective method to screen sodium-based layered materials for sodium ion batteries (一种筛选钠离子电池钠基层状材料的有效方法)
Xu Zhang, Zihe Zhang, Sai Yao, An Chen, Xudong Zhao & Zhen Zhou
npj Computational Materials 4:13 (2018)
doi:10.1038/s41524-018-0070-2
Published online:20 March 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
摘要:由于锂的成本高昂和资源不足,钠离子电池因而得到了广泛研究以便大规模应用。通常,插入型材料比合金型和转换型材料具有更好的循环稳定性。因此,本研究提出了一种简便有效的方法来筛选基于材料项目数据库的钠基层状材料,作为钠离子电池插入型的潜在候选材料。所获得的Na基层状材料包含38种空间群,表明本筛选方法的可信度不受空间群影响。然后,通过密度泛函理论计算,进一步研究了代表性材料的一些重要指标,包括平均电位、体积变化和钠离子迁移率。找到了一些体积变化和钠扩散能垒均很低的材料,它们有望成为钠离子电池候选电极。我们相信,本分类算法也可用于搜索其他基于碱金属离子和多价离子脱嵌的层状材料,加速电池材料的开发。
Abstract:Due to the high cost and insufficient resource of lithium, sodium-ion batteries are widely investigated for large-scale applications. Typically, insertion-type materials possess better cyclic stability than alloy-type and conversion-type ones. Therefore, in this work, we proposed a facile and effective method to screen sodium-based layered materials based on Materials Project database as potential candidate insertion-type materials for sodium ion batteries. The obtained Na-based layered materials contains 38 kinds of space group, which reveals that the credibility of our screening approach would not be affected by the space group.Then, some important indexes of the representative materials, including the average voltage, volume change and sodium ion mobility, were further studied by means of density functional theory computations. Some materials with extremely low volume changes and Na diffusion barriers are promising candidates for sodium ion batteries. We believe that our classification algorithm could also be used to search for other alkali and multivalent ion-based layered materials, to accelerate the development of battery materials.
Editorial Summary
Sodium-ion batteries: searching for layered electrode materials (钠离子电池:寻找层状电极材料)
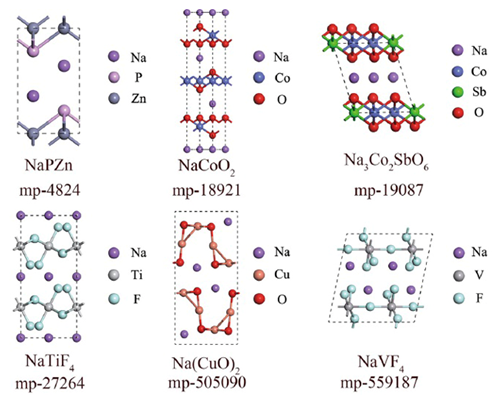
本研究开发的电脑程序能够筛选出有前景的电极材料,使得钠离子电池进入市场应用仅一步之遥(钠离子电池还无法进入市场)。来自中国南开大学的周震教授等,开发了一种快速的“高通量”计算方法,以搜索大量在线“材料项目”数据库中的层状钠基材料。确定该方案后,他们通过计算其储能特性(如体积变化和钠离子迁移率),来评估候选材料在钠离子电池中的潜在应用,发现数据库中的一些材料,包括Na(CuO)2、NaTiF4、Na2Zr(CuS2)2、Na3Co2SbO6和Na2Cu(CO3)2,可能适合用作'嵌入式'正极材料。作者希望此法也可以用于搜索其他类型的层状化合物作为电极材料,并希望以此加速新一代电池的开发。
Sodium-ion batteries are one step closer to market thanks (?)to a computer program that screens for promising electrode materials. A team led by Zhen Zhou at Nankai University in China developed a rapid, ‘high-throughput’ computational approach to search the vast online ‘Materials Project’ database for layered sodium-based materials.Once identified, the authors assessed the candidate materials’ potential for use in sodium-ion batteries by calculating their energy storage properties, such as volume change and sodium ion mobility, finding that a number of them-including Na(CuO)2, NaTiF4, Na2Zr(CuS2)2, Na3Co2SbO6, and Na2Cu(CO3)2–are potentially suitable for use as ‘insertion-type’ cathode materials. The authors hope their method could also be used to search for other types of layered compounds for electrode materials, and accelerate the development of next-generation batteries.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号