 Review on modeling of the anode solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) for lithium-ion batteries(锂离子电池阳极固体电解质界面(SEI)模拟研究进展)
Review on modeling of the anode solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) for lithium-ion batteries(锂离子电池阳极固体电解质界面(SEI)模拟研究进展)
Aiping Wang, Sanket Kadam, Hong Li, Siqi Shi & Yue Qi
npj Computational Materials 4:15(2018)
doi:10.1038/s41524-018-0064-0
Published online:26 March 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
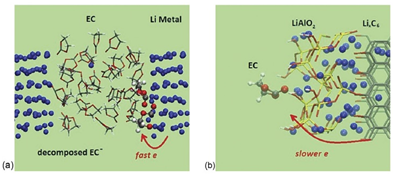
摘要:固体电解质界面(SEI)是由电解质的分解产物在电极表面上形成的钝化层。SEI允许Li +传输但阻挡电子通过,以防止电解质进一步分解,并确保电化学反应能够持续进行。由于其复杂的结构,及缺乏可靠的原位实验技术,SEI纳米厚度膜的形成和生长机理尚未完全明了。计算方法方面的重大进展使得SEI形成机制的预测模拟成为可能。本文旨在从电子结构计算到介观尺度模拟,涵盖电解质还原反应的热力学和动力学、SEI形成、通过电解质设计改性、SEI性质与电池性能间的关联,以及人工SEI设计方面来概述阳极上SEI膜研究的最新模拟进展。本文还对多尺度模拟作了总结和比较,并与实验结果进行比较。本文还讨论了SEI基本性质的计算细节,如:电子隧道效应、锂离子传输、块体SEI和电极/(SEI/)电解质界面的化学/机械稳定性。该综述展示了计算方法在SEI特性解析和人工SEI设计中的应用潜力。我们相信,计算建模与实验相结合可以相互补充,从而更好地了解SEI的复杂性,以便将来开发高性能电池。
Abstract:A passivation layer called the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) is formed on electrode surfaces from decomposition products of electrolytes. The SEI allows Li+ transport and blocks electrons in order to prevent further electrolyte decomposition and ensure continued electrochemical reactions.The formation and growth mechanism of the nanometer thick SEI films are yet to be completely understood owing to their complex structure and lack of reliable in situ experimental techniques.Significant advances in computational methods have made it possible to predictively model the fundamentals of SEI.This review aims to give an overview of state-of-the-art modeling progress in the investigation of SEI films on the anodes, ranging from electronic structure calculations to mesoscale modeling, covering the thermodynamics and kinetics of electrolyte reduction reactions, SEI formation, modification through electrolyte design, correlation of SEI properties with battery performance, and the artificial SEI design.Multi-scale simulations have been summarized and compared with each other as well as with experiments.Computational details of the fundamental properties of SEI, such as electron tunneling, Li-ion transport, chemical/mechanical stability of the bulk SEI and electrode/(SEI/) electrolyte interfaces have been discussed.This review shows the potential of computational approaches in the deconvolution of SEI properties and design of artificial SEI.We believe that computational modeling can be integrated with experiments to complement each other and lead to a better understanding of the complex SEI for the development of a highly efficient battery in the future.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号