 Improved phase field model of dislocation intersections (位错相交的改进相场模型)
Improved phase field model of dislocation intersections (位错相交的改进相场模型)
Songlin Zheng, Dongchang Zheng,Yong Ni & Linghui He
npj Computational Materials 4:20 (2018)
doi:10.1038/s41524-018-0075-x
Published online:11 April 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
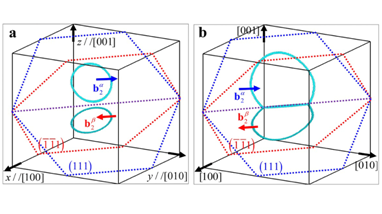
摘要:本研究揭示相交位错之间的长程弹性相互作用和短程芯结构反应,对于理解晶态固体中基于位错的应变硬化机制来说至关重要。相场模型通过使用连续统细观弹性理论来描述弹性相互作用,并将γ-表面结合到晶体能中,以使位错芯结构反应成为可能,因而在位错动力学建模中显示出巨大的潜力。由于在以前的相场模型中,晶体能近似表示为各滑移平面的层间势的线性叠加,所以它不能完全考虑滑移相交时滑移位错之间的反应。在本研究中,通过耦合两个相交滑移面的层间势来更新晶体能,提出了一种改进的模拟位错相交的相场模型,将其应用于共线位错相互作用研究,并与之前采用离散位错动力学模拟的结果进行比较。结果发现,仅改进的相场模型可以描述共线湮灭,并发现共线湮灭强烈地影响了多滑移系统中的位错锁结构形成和塑性流动。研究结果显示当前的改进对相场模拟位错相交是必要的。
Abstract:Revealing the long-range elastic interaction and short-range core reaction between intersecting dislocations is crucial to the understanding of dislocation-based strain hardening mechanisms in crystalline solids.Phase field model has shown great potential in modeling dislocation dynamics by both employing the continuum microelasticity theory to describe the elastic interactions and incorporating the γ-surface into the crystalline energy to enable the core reactions. Since the crystalline energy is approximately formulated by linear superposition of interplanar potential of each slip plane in the previous phase field model, it does not fully account for the reactions between dislocations gliding in intersecting slip planes.In this study, an improved phase field model of dislocation intersections is proposed through updating the crystalline energy by coupling the potential of two intersecting planes, and then applied to study the collinear interaction followed by comparison with the previous simulation result using discrete dislocation dynamics.Collinear annihilation captured only in the improved phase field model is found to strongly affect the junction formation and plastic flow in multislip systems. The results indicate that the improvement is essential for phase field model of dislocation intersections.
Editorial Summary
Phase field: Predicting dislocation interactions (相场:预测位错相互作用)
改进的相场建模方法可以更好地预测金属晶体的位错相互作用和塑性流动。中国科学技术大学倪勇教授团队对相场模拟中的晶体能量项作了改进,以便在立方金属中滑移面相交时能考虑滑移位错间相互作用。在新的相场模拟中,晶体能修改后成功地描述了应变硬化中最强的位错相互作用:共线相互作用过程中的位错湮灭现象。这种位错湮灭只有在改进的相场模型中被预测到。看来,对相场建模相关的能量项所作的改进,可以帮助我们更好地理解位错的行为并预测材料变形。
An improved phase field modeling approach can better predict dislocation interactions and plastic flow in metallic crystals. A team led by Young Ni at the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, China modified the crystalline energy term in phase field simulations to take into account interactions between dislocations gliding in intersecting slip planes in cubic metals.In simulations, the modified crystalline term successfully led to the annihilation of dislocations for the strongest type of interactions contributing to strain hardening, collinear interactions.This dislocation annihilation was only seen with the improved phase field model and not the conventional phase field model. Improvements in the expression of the energies associated with phase field modeling may help us better understand dislocation behavior and predict material deformation.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号