 Phase-field model of pitting corrosion kinetics in metallic materials(金属材料点腐蚀动力学的相场模型)
Phase-field model of pitting corrosion kinetics in metallic materials(金属材料点腐蚀动力学的相场模型)
Talha Qasim Ansari, Zhihua Xiao, Shenyang Hu, Yulan Li, Jing-Li Luo & San-Qiang Shi
npj Computational Materials 4:38 (2018)
doi:s41524-018-0089-4
Published online:24 july 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
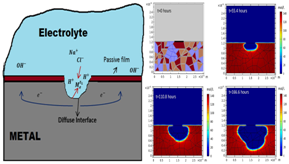
摘要:点腐蚀是最具破坏性的腐蚀形式之一,可导致结构的灾难性破坏。本研究提出了一种热力学一致性相场模型,用以定量预测金属材料中的点腐蚀动力学。引入一个序参数来表示金属-电解质系统内金属的物理状态。系统的自由能由离子浓度和序参数来描述。电解质中的离子传输和在电解质/金属界面处的电化学反应都被明确地包含在分析当中。离子浓度分布和序参数随时间的演变,是由系统的总自由能的减少而驱动,通过数值求解控制方程而获得。为了用实验校准本模型,我们建立了腐蚀过电位和动力学金属界面参数的直接关系。本模型被用于研究几个腐蚀问题,如两个点腐蚀坑间距的影响、残余应力的作用、陶瓷颗粒增强钢的腐蚀行为及其晶体取向对腐蚀速率的作用。
Abstract:Pitting corrosion is one of the most destructive forms of corrosion that can lead to catastrophic failure of structures. This study presents a thermodynamically consistent phase field model for the quantitative prediction of the pitting corrosion kinetics in metallic materials.An order parameter is introduced to represent the local physical state of the metal within a metal-electrolyte system.The free energy of the system is described in terms of its metal ion concentration and the order parameter.Both the ion transport in the electrolyte and the electrochemical reactions at the electrolyte/metal interface are explicitly taken into consideration.The temporal evolution of ion concentration profile and the order parameter field is driven by the reduction in the total free energy of the system and is obtained by numerically solving the governing equations.A calibration study is performed to couple the kinetic interface parameter with the corrosion current density to obtain a direct relationship between overpotential and the kinetic interface parameter.The phase field model is validated against the experimental results, and several examples are presented for applications of the phase-field model to understand the corrosion behavior of closely located pits, stressed material, ceramic particles-reinforced steel, and their crystallographic orientation dependence.
Editorial Summary
Corrosion: phase field method reproduces complex situations(腐蚀:相场法再现复杂情况)
本研究通过建立包含阳极和阴极反应的相场模型,可以成功地模拟金属材料的腐蚀。来自香港理工大学的石三强教授领导的团队,用相场法模拟金属腐蚀形貌的演变,研究了不锈钢浸入温和盐水后的点腐蚀坑的生长。作者开发了几种方程式,考虑了多种离子的迁移和浓度因素,引入了一个序参数来描述腐蚀界面的变化。由此构建的模型模拟了从介观到宏观尺度的腐蚀过程,成功地演示了两个腐蚀坑可以聚结形成更宽的腐蚀坑,残余应力的作用,以及腐蚀沿不同晶体取向的发展速率。这个模型可以被用于研究扩散控制,或者界面反应控制的腐蚀过程。成功地模拟复杂的腐蚀过程,可以帮助我们更好地理解腐蚀并减少其影响。
Stainless steel corrosion can be successfully simulated using a phase field model that takes into account anodic and cathodic reactions. A team led by San Qiang Shi at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University adapted a phase field method used for simulating metallic microstructure evolution to study corrosive pit growth in stainless steel immersed in mildly salted water.The authors developed equations taking into account the transport and concentration of ionic species and introduced a orderparameter to describe the changing corrosion interface.The resulting model simulated the corrosion process from the meso- to the macroscale, and successfully showed that two pits can coalesce to form a wider pit, and that residual stress affected corrosion rate, while corrosion occurred preferentially along specific crystallographic planes.Successfully simulating complex corrosion process may help usbetter understand its mechanisms and lessen its impact.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号