 Machine-learning the configurational energy of multicomponent crystalline solids (采用机器学习表述多组分结晶固体的构型能)
Machine-learning the configurational energy of multicomponent crystalline solids (采用机器学习表述多组分结晶固体的构型能)
Anirudh Raju Natarajan & Anton Van der Ven
npj Computational Materials 4:56 (2018)
doi:s41524-018-0110-y
Published online:01 November 2018
Abstract| Full Text | PDF OPEN
摘要:神经网络和高斯过程回归等机器学习工具被越来越多地用于原子作用势的研究。本研究开发了一种计算方法,借助这些非线性插值工具来描述多组分固体中依赖格点位置占据几率的性质。我们用对称性匹配集团函数来区分不同的局域有序度。以这些局部特征作为神经网络的输入,能够获得位点能量等局域性质。应用该技术,我们再现了多体相互作用的综合集团扩展哈密顿量,以及利用第一原理计算得到的锂嵌入TiS2的形成能。本研究给出的计算方法和结果表明,复杂的多体相互作用可以用非线性模型来近似得到,且拟合仅需通过较小的集团即可完成。
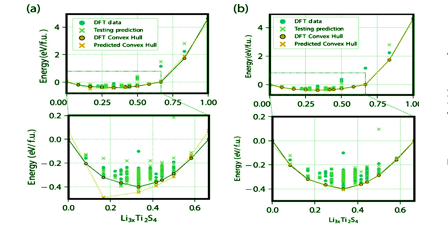
Abstract:Machine learning tools such as neural networks and Gaussian process regression are increasingly being implemented in the development of atomistic potentials. Here, we develop a formalism to leverage such non-linear interpolation tools in describing properties dependent on occupation degrees of freedom in multicomponent solids. Symmetry-adapted cluster functions are used to differentiate distinct local orderings. These local features are used as input to neural networks that reproduce local properties such as the site energy. We apply the technique to reproduce a synthetic cluster expansion Hamiltonian with multi-body interactions, as well as the formation energies calculated from first-principles for the intercalation of lithium into TiS2. The formalism and results presented here show that complex multi-body interactions may be approximated by non-linear models involving smaller clusters.
Editorial Summary
Machine learning: formation energy of crystals from neural network implementation (机器学习:神经网络方法计算晶体形成能)
基于机器学习工具可以得到晶体构型有序度的有效描述符。来自加州大学圣巴巴拉分校Anton Van der Ven领导的团队,开发了一种先进的神经网络方法,借助适度数量的关联函数作为描述符,构建了精确的格点哈密顿模型。利用位点中心关联函数作为描述符,该方法精确地得到面心立方晶体的综合多体二元哈密顿函数的形成能,以及锂插层TiS2的形成能。结果表明,复杂的多体相互作用可由非线性模型来近似描述,该描述借助较小的集团即可获得。该方法可以进一步拓展用于描述多组分晶体中给定构型自由度下任意的标量性质(包括形成能和体积)。
Robust descriptors of the degree of configurational order in a crystal can be formulated using machine learning tools. A team led by Anton Van der Ven at University of California, Santa Barbara, developed an advanced neural network implementation to build accurate lattice model Hamiltonians using a moderate number of correlation functions as descriptors. Using site-centric correlation function descriptors, the formalism can accurately model the formation energies of a synthetic multi-body binary Hamiltonian on face centered cubic crystals, as well as on Li-intercalated TiS2. As a result, complex multi-body interactions may be approximated by non-linear models involving smaller clusters. The approach can be generalized to describe any scalar property of a multi-component crystal, including its formation energy and volume, as a function of the configurational degrees of freedom.


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号