Coherent and semicoherent α/β interfaces in titanium: Structure, thermodynamics, migration
Siqi Wang, Tongqi Wen, Jian Han & David J. Srolovitz
npj Computational Materials 9: 216 (2023). Published: 07 December 2023
Editorial Summary
Deep Potential: Investigating the Structure and Thermodynamic Properties of Titanium Alloy α/β Interfaces
Titanium alloys, renowned for their exceptional performance and wide-ranging applications, require optimization of their α/β microstructure for enhanced properties. The key to alloy performance, interface energy, presents significant measurement challenges. Emerging technologies, including thermodynamic integration and neural network models trained on DFT data, now enable precise calculations of interface energy, thereby opening a new chapter in material design and performance optimization.A team lead by Prof. Jian Han from Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, investigated the structure and thermodynamics of theα/βinterface in Ti using molecular dynamics, thermodynamic integration and a DFT-trained Deep Potential. The authors first focus on the thermodynamic properties of the coherentα/βinterface in titanium (i.e.,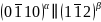 and
and 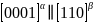 ) as a function of strain and temperature. Next, the authors examine the structure and properties of the semicoherent interface. This information is then applied to understand the nucleation and growth ofαprecipitates in aβmatrix (i.e., cooling from high temperature). The main findings in this paper are as follows. (i) The authors predict the free energy of the most important interfaces (coherent and semicoherent) in titanium. This represents the first such calculations with DFT-level accuracy (note thatβphase is completely unstable at 0 K and hence inaccessible to DFT without artificial constraints). (ii) The simulations show the equilibrium structure of the semicoherent interface and its intrinsic defect structure that gives rise to the widely-observed habit plane. (iii) The authors demonstrate the mechanism of interface migration and that this mechanism gives rise to different interface mobilities in different directions (heating vs. cooling). (iv) These accurate thermodynamic and structural results are applied to make reliable predictions on how precipitation occurs upon cooling through theα-βphase transition. This paper provides a roadmap for accurate prediction of interface properties and motion as well as precipitation in any system, including in systems with phases that are unstable at low temperature and in systems where loss of coherency occurs.
) as a function of strain and temperature. Next, the authors examine the structure and properties of the semicoherent interface. This information is then applied to understand the nucleation and growth ofαprecipitates in aβmatrix (i.e., cooling from high temperature). The main findings in this paper are as follows. (i) The authors predict the free energy of the most important interfaces (coherent and semicoherent) in titanium. This represents the first such calculations with DFT-level accuracy (note thatβphase is completely unstable at 0 K and hence inaccessible to DFT without artificial constraints). (ii) The simulations show the equilibrium structure of the semicoherent interface and its intrinsic defect structure that gives rise to the widely-observed habit plane. (iii) The authors demonstrate the mechanism of interface migration and that this mechanism gives rise to different interface mobilities in different directions (heating vs. cooling). (iv) These accurate thermodynamic and structural results are applied to make reliable predictions on how precipitation occurs upon cooling through theα-βphase transition. This paper provides a roadmap for accurate prediction of interface properties and motion as well as precipitation in any system, including in systems with phases that are unstable at low temperature and in systems where loss of coherency occurs.
编辑概述
深度学习势函数:研究钛合金α/β界面结构与热力学性质
钛合金因其卓越的性能和广泛应用,对其α/β微观结构的优化至关重要。界面能量是影响合金性能的关键,但直接测定其值极具挑战。新兴技术,包括热力学积分和基于DFT数据的神经网络模型,现已使得界面能量的精确计算成为可能,进而推动了材料设计和性能优化的新篇章。由香港城市大学材料科学与工程系的Jian Han教授领导的团队,采用分子动力学、热力学积分以及经过密度泛函理论(DFT)训练的深度学习势模型,深入探讨了钛材料中α/β界面(即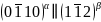 和
和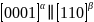 ))的结构和热力学特性。研究首先集中于分析钛的相干α/β界面的热力学性质,并考察其如何受到应变和温度的影响。随后,团队对半相干界面的结构和属性进行了细致审查,并将这些发现用于理解β基体中α析出相的成核及生长过程,也就是从高温状态开始的冷却过程。该论文的关键发现包括:(1)成功预测了钛中最关键界面(相干和半相干)的自由能,这是首次以接近DFT精确度进行此类计算(值得注意的是,β相在0K下完全不稳定,因而在没有人为约束的情况下DFT无法直接计算);(2)模拟结果展示了半相干界面的平衡结构和本质的缺陷结构,这些结构解释了习惯面的普遍存在;(3)揭示了界面迁移的作用机理,并指出这一机理在不同方向(比如升温与降温)会导致界面迁移速率的不同;(4)这些精确的热力学和结构数据被用于可靠预测α-β相变冷却过程中析出相的形成。此项研究不仅为准确预测界面属性和运动提供了指导,还为理解和预测包括在低温下不稳定的相和相干性丧失情况下的析出行为提供了实用的参考。
))的结构和热力学特性。研究首先集中于分析钛的相干α/β界面的热力学性质,并考察其如何受到应变和温度的影响。随后,团队对半相干界面的结构和属性进行了细致审查,并将这些发现用于理解β基体中α析出相的成核及生长过程,也就是从高温状态开始的冷却过程。该论文的关键发现包括:(1)成功预测了钛中最关键界面(相干和半相干)的自由能,这是首次以接近DFT精确度进行此类计算(值得注意的是,β相在0K下完全不稳定,因而在没有人为约束的情况下DFT无法直接计算);(2)模拟结果展示了半相干界面的平衡结构和本质的缺陷结构,这些结构解释了习惯面的普遍存在;(3)揭示了界面迁移的作用机理,并指出这一机理在不同方向(比如升温与降温)会导致界面迁移速率的不同;(4)这些精确的热力学和结构数据被用于可靠预测α-β相变冷却过程中析出相的形成。此项研究不仅为准确预测界面属性和运动提供了指导,还为理解和预测包括在低温下不稳定的相和相干性丧失情况下的析出行为提供了实用的参考。


 沪公网安备 31010502006565号
沪公网安备 31010502006565号